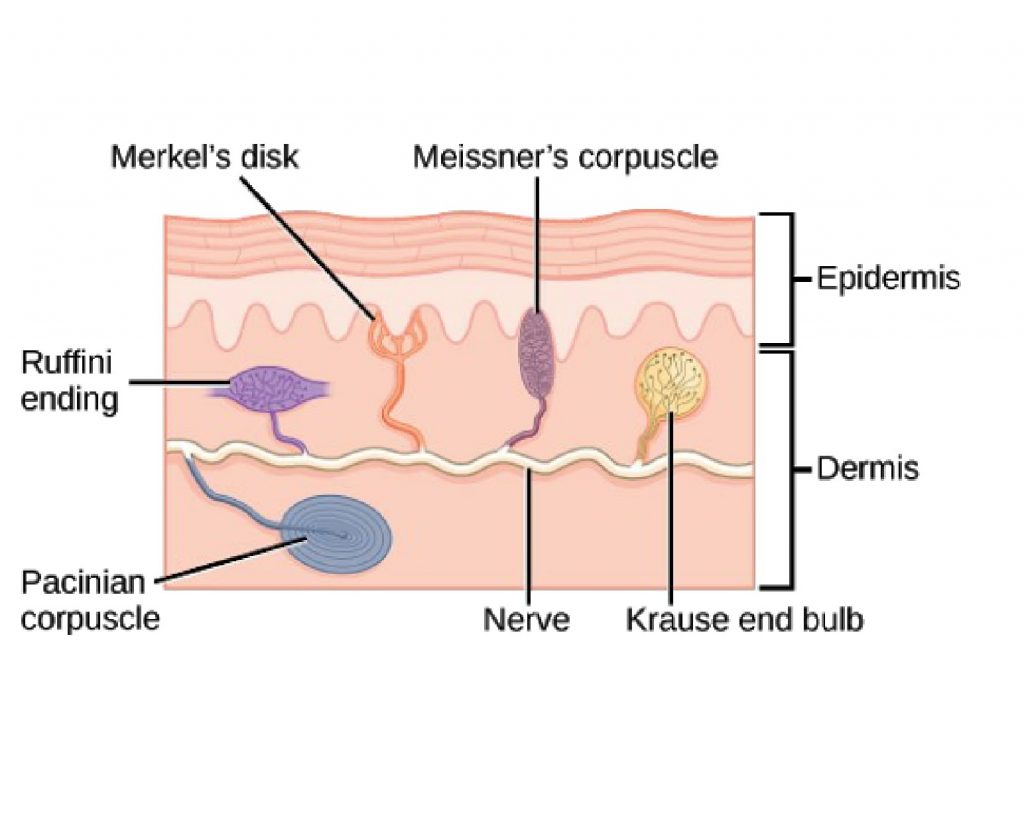
Receptor is a specialized modified sensory nerve ending which undergoes depolarization in response to a specific stimulus and in turn sends information to the CNS. It’s function is to act as a transducer to convert various forms of energy into electric energy in Neuron. Each type of sensation (pain, touch, vibration etc) is called modality …
Open blog
Uterus is supported and prevented from sagging down by many factors which are chiefly muscular and fibromuscular. PRIMARY SUPPORTS MUSCULAR OR ACTIVE SUPPORTS Pelvic diaphragm. Perineal body. Distal urethral sphincter mechanism. FIBROMUSCULAR OR MECHANICAL SUPPORTS Uterine axis. Pubocervical ligaments. Transverse cervical ligaments of Mackenrodt. Uterosacral ligaments. Round ligaments of uterus SECONDARY SUPPORTS Broad ligaments. Vesicourethral …
Hi, let’s learn something about deglutition Deglutition (swallowing) is the process by which food moves from mouth into the stomach. There are 3 stages or phases of deglutition 1) Voluntary stage 2) Pharyngeal stage 3) Esophageal stage Voluntary Stage Pharyngeal Stage Esophageal Stage Nervous Regulation (Deglutition reflex) Applied Physiology Voluntary Stage Also known as oral …
What is the GFR? It is the ultra-filtration of plasma in the glomerulus. The glomerular filtration rate is the amount of blood filtered by the kidney’s glomerulus into the bowman’s capsule per unit of time. It is abbreviated as GFR. Its normal value is 125ml/min or 180L/24 hours. The rate of filtration is influenced by …
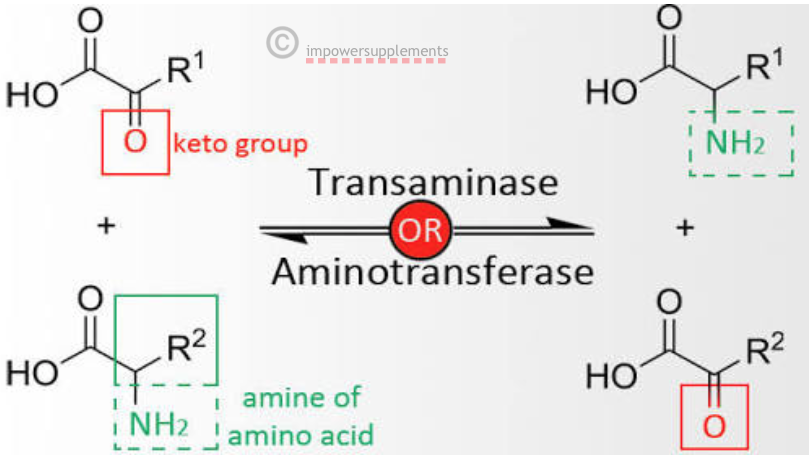
TRANSAMINATION What is transamination? The transfer of an amino group from an amino acid to a keto acid is known as transamination. It is catalysed by a group of enzymes called transaminases (recently aminotransferases) What is the mechanism of transamination? Occurs in two stages Transfer of the amino group to the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) …
Features: Endocrine gland Consists of right and left lobe connected by an isthmus Functions: Regulates basal metabolic rate Stimulates psychic and somatic growth Regulates calcium metabolism. Being one of the important glands in our body, we have to know everything about this gland in detail. We are going to cover the following: Situation and Extent …
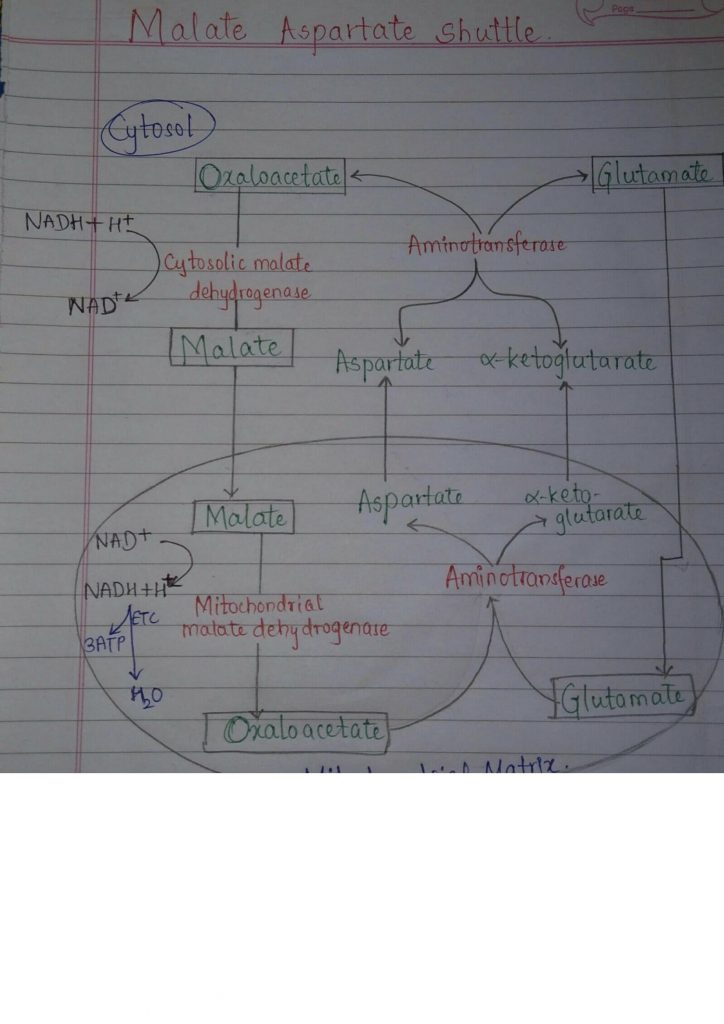
The process of synthesizing ATP from ADP & Pi coupled with electron transport chain is known as oxidative phosphorylation. For this oxidation to take place, many components are required. One of them is NADH, the reducing equivalent. Transport of reducing Equivalents – the shuttle pathways. The inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to …
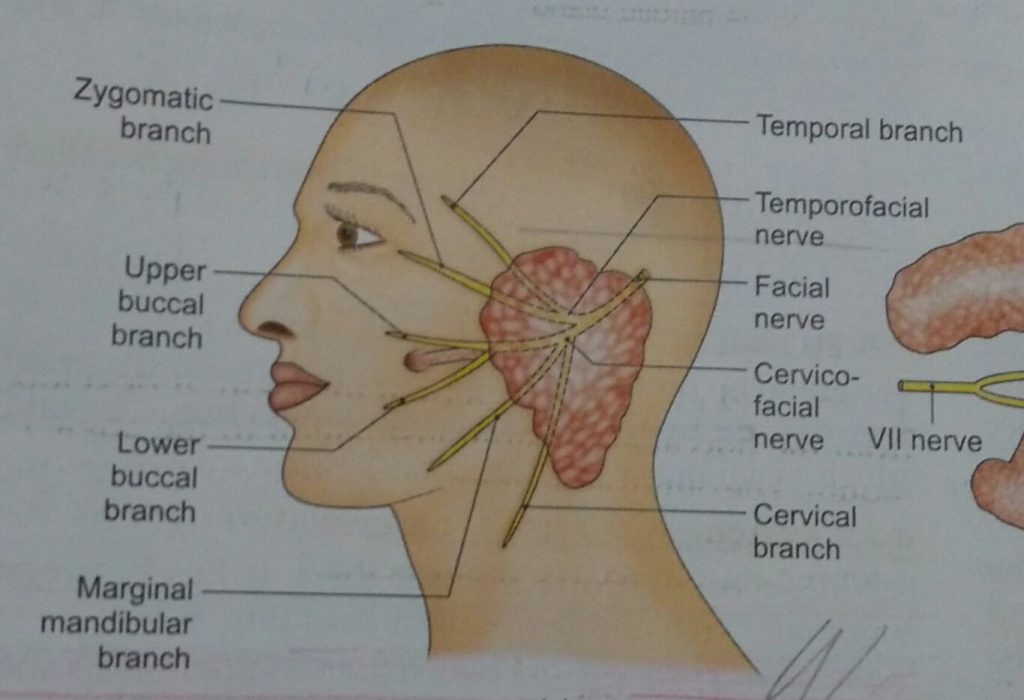
Parotid Gland Imp features – Largest salivary gland. Situated between ESR– external acoustic meatus, ramus of mandible & sternocleidomastoid. Capsule – Formed by investing layer of deep cervical fascia, which splits to enclose the gland. Capsule – Superficial and Deep Lamina Thick Thin Adherent to gland. Attached to styloid process, Zygomatic arch, tympanic plate. External …