Introduction It is the 9th cranial nerve It is the nerve of 3rd branchial arch Supply Sensory to Pharynx, Tonsil, Soft Palate, posterior 1/3rd of Tongue, Carotid body & Carotid Sinus (PPTTCC) Motor to Stylopharyngeus Secreto-motor to Parotid Gland Gustatory to tongue and circumvallate papillae Nuclei Functional Components Branches Tympanic branch Lingual branch Carotid branch …
ANATOMY OPEN BLOG
Corpus callosum What is Corpus callosum? It is the connective pathway between the left and the right side of the brain. It is responsible for transmitting neural messages between both the hemispheres The corpus callosum sits in the centre of the brain, measures around 10 cm in length and is shaped like the letter C …
Median Osseocartilenous portion b/w the two nasal halves of nasal cavity. Forms a mucus membrane covered medial wall of both nasal cavities. Because of world functions on dominance, so does our nasal septum. There is rarely strictly median septum. Deviation occurs due to over growth of one of the side thus deflecting the septum towards …
Uterus is supported and prevented from sagging down by many factors which are chiefly muscular and fibromuscular. PRIMARY SUPPORTS MUSCULAR OR ACTIVE SUPPORTS Pelvic diaphragm. Perineal body. Distal urethral sphincter mechanism. FIBROMUSCULAR OR MECHANICAL SUPPORTS Uterine axis. Pubocervical ligaments. Transverse cervical ligaments of Mackenrodt. Uterosacral ligaments. Round ligaments of uterus SECONDARY SUPPORTS Broad ligaments. Vesicourethral …
Features: Endocrine gland Consists of right and left lobe connected by an isthmus Functions: Regulates basal metabolic rate Stimulates psychic and somatic growth Regulates calcium metabolism. Being one of the important glands in our body, we have to know everything about this gland in detail. We are going to cover the following: Situation and Extent …
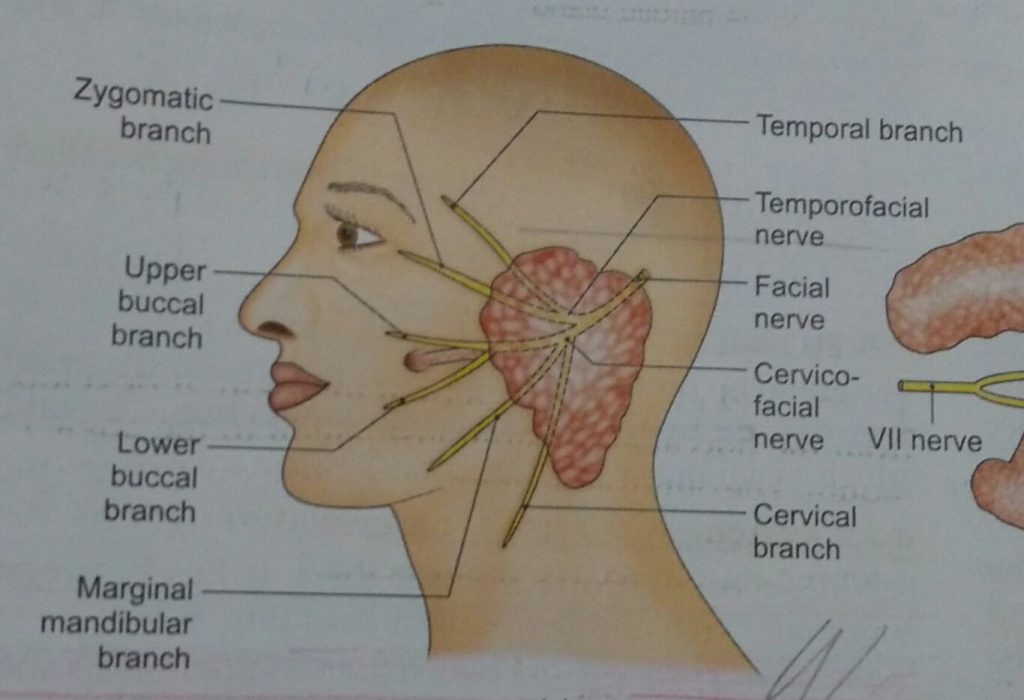
Parotid Gland Imp features – Largest salivary gland. Situated between ESR– external acoustic meatus, ramus of mandible & sternocleidomastoid. Capsule – Formed by investing layer of deep cervical fascia, which splits to enclose the gland. Capsule – Superficial and Deep Lamina Thick Thin Adherent to gland. Attached to styloid process, Zygomatic arch, tympanic plate. External …