Introduction
Middle Ear is an air-filled, mucous membrane lined space in the Petrous Temporal bone, between the internal and external ear. It is also called the Tympanic cavity/ Tympanum.
Subdivided into-
1-Tympanic cavity proper-opposite the tympanic membrane
2-Epitympanic recess-above the level of tympanic membrane
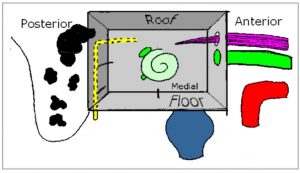
Shape
Like a cube compressed from side to side, with large lateral and medial walls, while other walls are narrow.
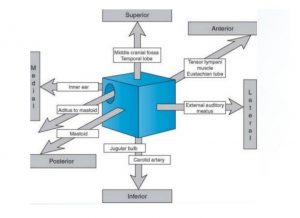
Boundaries
It has a roof, floor, anterior, posterior, medial and lateral walls.
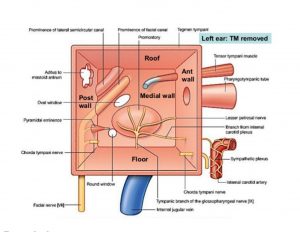
1.Tegmental wall / Roof-
Consists of thin layer of bone- Tegmen tympani. Separates the middle ear from the middle cranial fossa.
2.Jugular wall / Floor-
Thin layer of bone which separates it from the Internal Jugular vein. Near medial border of floor, through a small aperture, tympanic branch of Glossopharyngeal nerve enters.
3.Membranous / Lateral wall-
Consists almost entirely of the tympanic membrane. In upper part, consists of lateral wall of epitympanic recess.
4.Mastoid / Posterior wall-
It is only partially complete. In lower part, bony partition between tympanic cavity and mastoid air cells. Superiorly, epitympanic recess is continuous with aditus to Mastoid antrum.
Structures related
- Pyramidal eminence-elevation for entry of Stapedius
- Opening for entry of Chorda Tympani
5.Carotid/ Anterior wall-
Partially complete. In lower part, thin layer of bone separating tympanum from Internal Carotid artery.
Structures related
- Opening for Pharyngotympanic tube
- Smaller opening for canal containing tensor tympani
- Foramen for exit of Chorda Tympani
6.Labyrinthine/ Medial wall-
forms lateral wall of internal ear.
Most prominent structure is a round bulge.
Promontory formed by base of cochlea,which has an associated plexus of nerves- Tympanic plexus.
Tympanic plexus is formed by tympanic branch of Glossopharyngeal nerve – branches from Internal Carotid Plexus
The Lesser petrosal nerve is a branch of the Tympanic plexus which leaves the middle ear from the foramen ovale to relay in Otic ganglion.
ALSO READ OTHER RELATED ARTICLES – Fascial layers of the neck and carotid sheath
Structures related
- Windows–
Oval window– Posterosuperior to promontory
Round window– Posteroinferior to promontory
- Prominences–
Prominence of Facial canal which is posterosuperior to the oval window.
Prominence of Lateral semicircular canal
Contents–
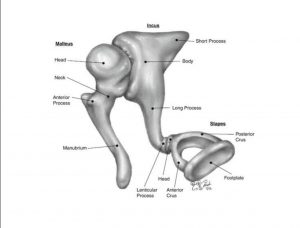
1.Three bone ossicles– Malleus, Incus, Stapes
2.Ligaments of ear ossicles
3.Muscles– Tensor tympani, Stapedius
4.Vessels
5.Nerves– Chorda Tympani, Tympanic Plexus
6.Air
Clinical anatomy-
1.Otitis media– infection of the middle ear cavity
2.Mastoiditis– infection of mastoid air cells
3.Vertigo– spinning sensation associated with Tinnitus(ringing, buzzing, other sounds)
4.Otosclerosis– changes with aging leading to hearing loss.
-Nikita Balani
More Articles-
Cholesterol synthesis mnemonic