Central Dogma Of Protein Synthesis: (By Crick)
DNA
↓
m-RNA
↓
Protein
Genetic Code:
Dictionary of nucleotide base combinations which determine sequence of amino acids in proteins.
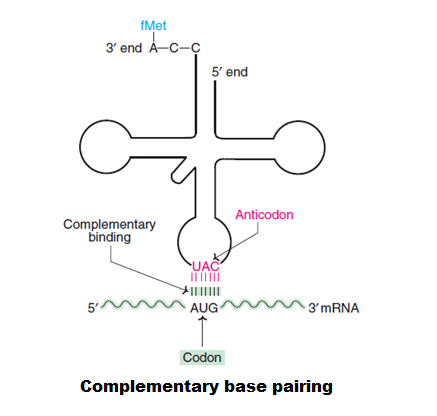
Codon:
A sequence of 3 nucleotide bases on m-RNA which
codes for a single amino acid. E.g. AUG codes for
methionine
(Number of Codons= 4 x 4 x 4 (Since there are 4 different nucleotide bases Purines: A, G Pyrimidines: C, U NOT T)
= 64
Holley, Khurana and Nirenberg:
Nobel for deciphering/ cracking the
genetic code
61 sense codons ― 20 standardamino acids
3 non-sense/stop codons― UAG-Amber
UGA-Opal
UAA-Ochre
(Selenocysteine is coded for by UGA, though it is a stop codon which depends on availability of selenium)
CHARACTERISTICS:
Read on m-RNA from 5’→3’ without gaps
One codon → One amino acid
Exception: AUG (start codon) →Methionine, but if AUG not available, GUG→Methionine
One amino acid→Multiple codons E.g.: GGG, GGA, GGC, GGU code for glycine
Same in all organisms from bacteria to mammals (exceptions are found in yeast mitochondria and mycoplasma)
Wobble Hypothesis:
- Since genetic code is degenerate, 61 codons code for 20 amino acids.
- BUT the number of t-RNA is NOT 61, but less. This is due to wobbling of 3rd base of codon.
- The 3rd base of t-RNA may not be complementary. Actual pairing occurs at 1st two positions only.
m-RNA: GUU GUC GUA GUG
t-RNA:CAA CAA CAA CAA
Amino: Val ValValVal
Acid
Single Gene Mutation:
Sickle Cell Anaemia: GAG → GUG,
Glu → Val ( At 6th position of β Chain of Hb)
Sickling under low oxygen tension
Frame Shift Mutation:
Addition/Deletion results in an altered reading frame resulting in:
- Altered amino acid sequence
- Premature termination of peptide chain resulting in dysfunctional/non-functional protein.
— Jay Shah