First, let us learn what is metabolism of xenobiotics..
- Detoxification –
The series of biochemical reactions occurring in the body to convert foreign compounds to non-toxic and more easily excretable form.
- Xenobiotic is any foreign or strange substance to the body.
- Detoxification of this is called metabolism of xenobiotics.
- The metabolism of xenobiotics is divided into 2 phases –
- Reactions are – oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis.
- Conjugation reactions.
Let us study conjugation in details.
Conjugation is a process in which a foreign substance combines with a substance produced in the body.
The combined product is then easily detoxified & excreted from the body.
- Few examples of important conjugating agents –
1.Glucuronic acid :
- This is the most common.
- The active form of glucoronic acid is UDP-glucoronic acid in uronic acid pathway.
- UDP-glucuronyltransferasesare the enzymes which participate in glucuronide formation.
- It occurs with compounds containing hydroxyl , carbonyl, sulfhydryl or amino groups.
- Strongly acidic compounds which are more soluble in water are produced – hence more easily excreted.
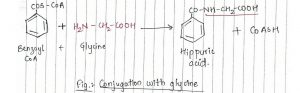
2.Glycine
- Aromatic carboxylic acids are conjugated with glycine.
- When benzoyl CoA is conjugated with glycine, hippuric acid is formed.
3.Glutamine :
- Is relatively less important.
- Phenylacetic acid is conjugated with glutamine to form phenylacetyl glutamine.
4.Methylgroup :
- Methyl group of S-adenosylmethionine is used to methylate many compounds.
Enzyme methyl transferase is used.
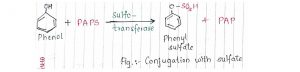
5.Sulfate:
- The active form 3’-phosphoadenosine 5- phosphosulfate(PAPS)participates in conjugation.
- Enzyme sulfotransferase in involved.
- Aliphatic & aromatic compounds undergo sulfation.
6.Acetic acid :
-Acetyl CoA is the active form .
– Drugs like sulfanilamide are converted to acetyl derivatives.
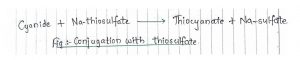
7.Thiosulfate :
- Highly toxic cyanides are conjugated with thiosulfate to form less toxic thiocyanate.
8.Glutathione :
- Glutathione is a tripeptide.
- A wide range of organic compounds such as alkyl or aryl halides, alkenes and epoxides are conjugated with cysteine of glutathione.
- The conversion of bilirubin to conjugated bilirubin is an example of conjugation with glucuronide.
- Bilirubin combines with UDP – glucuronic acid to form bilirubin-diglucuronide.
Contributed by
Soumya Khot- GMC, Kolhapur.