Elements with same atomic number (SAN) but different atomic weights (DAW).
There are two types of isotopes:
- Stable Isotopes
- Naturally occurring
- Do not emit radiations
- Identified and quantitated by mass spectrometry or nuclear magnetic resonance.
- Sometimes used in biochemical investigations.
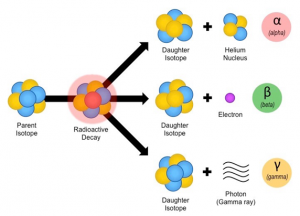
- Unstable or Radioactive Isotopes (IMP SAQ)
Nucleus unstable → Decay → αβ and gamma rays emission
Curie : Defined as the amount of radioactivity equivalent to 1 gm of radium (2.22 x 10 raised to 12) disintegration per minute.
Millicurie = 2.2 x 10 raise to 9
Microcurie = 2.2 x 10 raise to 6
- Geiger counters
- Liquid scintillation counter
- Autoradiography
- Determine metabolic origin of complex molecules like heme , cholesterol , purines and phospholipids.
- Determining the precursor-product relationship in metabolic pathways ex. Krebs cycle, urea cycle etc..
- Study of metabolic pools and metabolic turnovers.
- Endocrine and immunological studies
- To elucidate drug metabolism.
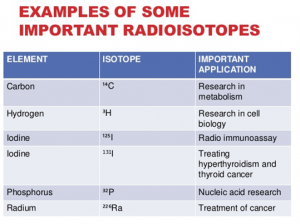
- Scanning of organs – thyroid 131I , bone 90Sr , kidney 131 I hippuran.
- Treatment of cancer